Search for Syntactical Constructs
The Construct tab offers additional items in the Construct palette when a syntax![]() The analysis of the function of each word in a clause or phrase database is installed. These are the CLAUSE and PHRASE items and the Syntactical term elements (if the appropriate Syntax resource
The analysis of the function of each word in a clause or phrase database is installed. These are the CLAUSE and PHRASE items and the Syntactical term elements (if the appropriate Syntax resource![]() Any Bible text, or other single tool that can be read in Accordance, including reference texts and articles; may also be referred to as content or module is installed). These items are used to define clauses or phrases, and to search for the syntactical terms either within the clause or phrase, or on their own.
Any Bible text, or other single tool that can be read in Accordance, including reference texts and articles; may also be referred to as content or module is installed). These items are used to define clauses or phrases, and to search for the syntactical terms either within the clause or phrase, or on their own.
When these items are dragged from the palette to a column, a dialog box opens for selecting a further definition of the item.
|
|
Hint Watch Dr. J's podcast about Understanding the Syntax for more information (based on Accordance V 11.1.3) |
| Syntax Items | Example of a Syntax Item Dialog Box |
|---|---|
|
|
The Scope of a Construct search is automatically set to “Chapter" when it includes a Syntax phrase or clause. The CLAUSE and PHRASE items each open a dialog box with further optional definitions.
Your choices are reflected in the label that appears in the clause or phrase item. The PHRASE item includes Phrase in its label.
|
|
Hint To quickly change the depth of a Phrase or Clause item, simply select the item and enter the desired number for the depth. |
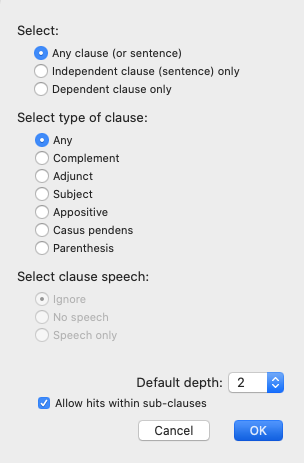
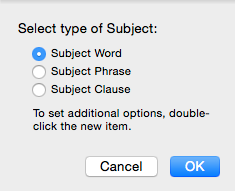
Clause: To define the Clause
- Select the type of clause: Any clause (or sentence), Independent clause (sentence) only, or Dependent clause only.
-
If an Independent clause (sentence) only, choose one of the items in the "Select type of clause" and/or the "Select clause speech" areas.
With regard to the clause speech, you may choose whether to ignore speech (Ignore), search only non-speech (No speech), or search speech only (Speech only).
- If a Dependent clause only, choose one of the items in the "Select type of clause" area.
-
Default depth determines how closely related the searched terms must be relative to this clause. The depth number indicates the number of extra levels of syntactical structure that may be present between the clause and its found search term. For example, a depth of zero requires the element be directly inside of the clause, while a depth of 6 allows for up to 6 levels of hierarchy to be present.
-
Allow hits within sub-clauses: If this option is selected, elements in other clauses will be included in the search. If the clause depth is set to 0, this setting is redundant.
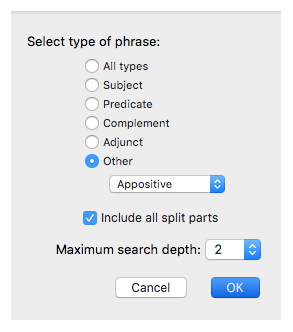
Phrase: To define the phrase, choose from the items listed below.
- Select type of phrase: Choose from
- All types
- Subject
- Predicate
- Complement
- Adjunct
- Other: This opens a pop-up menu for choosing Appositive, Vocative, or CasusPend.
- Phrase structure: Choose from:
- One segment: Your search will only consider one segment of a split phrase such as a predicate.
- All segments: Your search will consider all segments of a split phrase such as a predicate. This option will not find embedded phrases on the same level, such as a subject with parts of a predicate on both sides.
-
Contiguous: Your search will only use contiguous phrases.
Visual feedback in the form of a label has been added to the phrase item in a construct window, as follows:
- One segment: The label in inside parentheses.
- All segments: The label is unchanged.
-
Contiguous: The label has a bullet mark (•) before it.
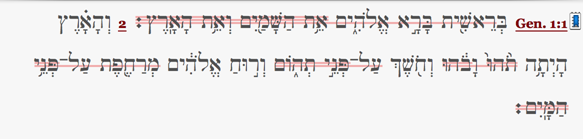
Referring to Genesis 1:1, an example of how to select the correct segment item is given below:
 Details about Choosing the Correct Segment Item
Details about Choosing the Correct Segment Item
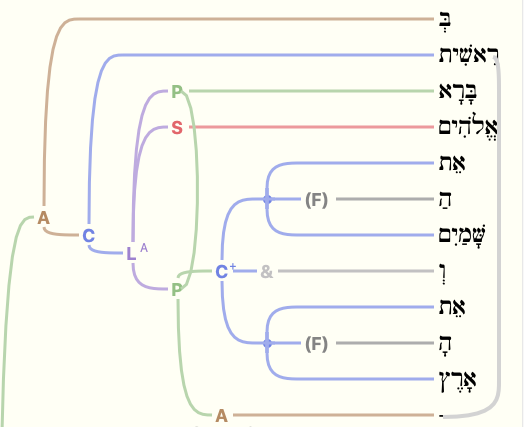
- All segments:For this example the predicate phrase contains both the verb (bara) and the complement (shamayim and aretz). Though every word that is part of the phrase falls under the same phrase container, this creates some problems when trying to find elements like the subject, elohim, which is located between phrases.
- One segment: This search finds any segment of a split phrase. However, the complete phrase will not be found when other syntactical elements intervene. In the example above, a search for a predicate phrase containing a predicate and a complement, if set to one segment, will not find Genesis 1:1, because the predicate item (bara) and complement item (aretz), exist in separate segments.
- Contiguous: This search only finds phrases that have no split in them. In the example above, the complement phrase is a contiguous phrase and will be found, but the predicate phrase contains an intervening subject and will not be found.
- Default depth: Determines how closely related the searched terms must be relative to this phrase. The depth number indicates the number of extra levels of syntactical structure that may be present between the phrase and its found search term. For example, a depth of zero requires the element be directly inside of the phrase while a depth of 6 allows for up to 6 levels of hierarchy to be present
- Allow hits within sub-clauses: If this option is selected, elements in other clauses will be included in the search. If the clause depth is set to 0, this setting is redundant.
- Clause and phrase items can only be added to empty columns.
- Each clause or phrase item initially contains two columns to allow for more than one word in the unit. Thus, when placed into a column it automatically expands it to two columns. This defines the unit as nested inside the unit above it.
- Drag the blue edge to adjust the number of columns within the unit. If the unit is placed within another unit, the columns in the enclosing unit adjust to match.
- Drag the bottom edge of the item to enlarge it.
- Moving or deleting a unit moves or deletes all items within the unit.
- Drag connecting commands into the Clause or Phrase unit to define the relationships between the columns of the unit.
- Connecting commands can only be used to link Clause or Phrase units at the same level.
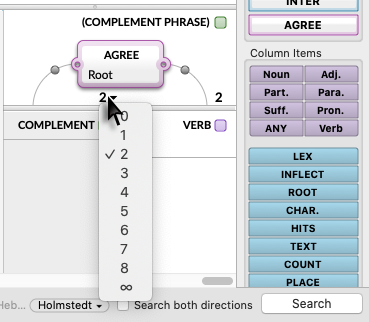
- Clause and phrase depth settings are adjusted by clicking on the number located above the columns.
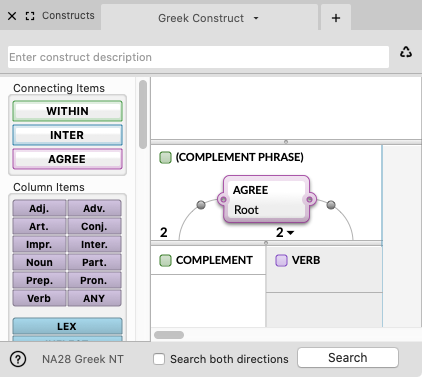
The picture below provides an example of a clause and phrase unit for a Greek construct.
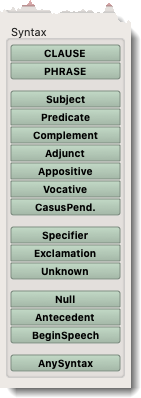
- For most syntactical elements you can select Any, Simple, or Compound. Simple adds -S to the name of the item in the column, and Compound adds -C.
- For the Null element, you can specify 1-3 adjacent Null tags. You cannot have Adjacent Null elements in the construct.
- Within a column these elements can be combined with any of the parts of speech or other element items.
- Antecedent and Begin Speech have no further qualifiers.
- Items placed directly in columns at the top level are found within the scope specified in the Search tab
 The core tab used to search Bible texts, it consists of a search entry area and a search results area (verse, sentence, etc).
The core tab used to search Bible texts, it consists of a search entry area and a search results area (verse, sentence, etc).
|
|
Note You must use the Chapter or Book field when using a Clause or Phrase item as many clauses stretch across verse boundaries. If Chapter or Book is not currently specified, the scope will automatically be set to Chapter. |
- Adjacent columns do not necessarily indicate adjacent words in the search results of a Construct, unless a WITHIN of 1 is used.
- Double-click any element to revise its definition, as in a regular construct.
- You may apply the syntactical term (such as adjunct) directly to the word, or define it on the phrase or clause enclosing it. The search results for the terms will differ depending on whether you search for a word or a unit containing the term.
The search results are displayed in all linked Search tab. Normally the words matching the search are marked with the highlight style for hit words![]() The verses, words, text, or other information found as the result of a search, with these differences:
The verses, words, text, or other information found as the result of a search, with these differences:
-
A search for a specific phrase or clause draws a line through the entire unit. For multiple hierarchical results, the lines will stack to easily see unit boundaries.
- Null hits are marked with a pin with a circle head.

- Antecedent hits are marked with a flag pointing backwards.

- Begin speech hits are marked with a flag pointing forwards.

- Searching for words which are subjects, predicates, complements, etc. highlights only the main subject, predicate, etc. and not all the subordinate items within the same clause.
- Begin Speech highlights the prior word.
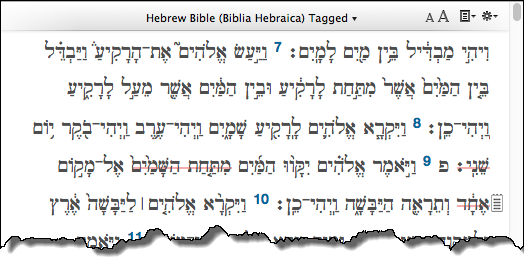
Search for Adjunct in Gen 1:
| Method | Search Term | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Search Entry Box of a Search Tab |
![Search for [ADJUNCT] in the Search Entry box Search for [ADJUNCT] in the Search Entry box](../../resources/images/adjunct1.png)
|

|
| Construct in any Sentence |

|
Same as above |
| Construct: Adjunct Phrase |

|
|
| Construct: Adjunct Clause |

|

|